How to Use jQuery AJAX for Dynamic Web Applications
- Samul Black

- Jul 27, 2025
- 5 min read
In the era of fast, responsive, and user-friendly web applications, jQuery's AJAX functionality remains a powerful tool for building dynamic interfaces. AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) allows your web page to communicate with the server without needing a full-page refresh, creating seamless user experiences.
With just a few lines of code, jQuery simplifies the process of sending and receiving data asynchronously, making it ideal for tasks like live search, form submissions, and updating content in real time. Whether you're fetching data from an API or posting a form silently in the background, jQuery's AJAX methods offer an easy and reliable approach to modern front-end development.
In this guide, we'll walk you through how to use jQuery's AJAX features effectively—from basic syntax to handling JSON responses, error handling, and practical examples you can apply in your own projects.

Introduction: Why jQuery AJAX Still Matters
In a world dominated by modern frontend frameworks and native APIs, it's easy to overlook the power of jQuery. Yet, jQuery’s AJAX functionality continues to hold strong—especially in scenarios where simplicity, speed, and compatibility are key. From quick prototypes to production-ready legacy applications, jQuery AJAX offers a reliable and efficient way to make asynchronous HTTP requests.
Its ease of use, minimal setup, and battle-tested methods make it ideal for developers who want to fetch or send data without refreshing the page. Whether you’re enhancing an existing project or building lightweight web apps, jQuery AJAX can help you add interactivity with minimal overhead.
Understanding AJAX: The Engine Behind Modern Web Interactions
AJAX stands for Asynchronous JavaScript and XML—a technique that allows web pages to communicate with a server without reloading the entire page. This capability enables modern web applications to feel smoother, faster, and more responsive.
Here’s how it works:
A user triggers an event (like clicking a button).
JavaScript sends a request to the server in the background.
The server processes the request and sends back data.
JavaScript then updates part of the web page with the new data—all without a page reload.
Before AJAX, traditional web apps required a full refresh for every interaction. Today, AJAX enables dynamic, real-time updates in everything from chat apps to live search, dashboards, and e-commerce carts.
Why Choose jQuery for AJAX Calls?
While modern JavaScript provides the Fetch API and third-party libraries like Axios, jQuery offers a cleaner, simpler abstraction that appeals to both beginners and experienced developers working on existing codebases.
Here’s why many developers still choose jQuery for AJAX:
Cross-browser Compatibility: jQuery smooths over browser inconsistencies.
Concise Syntax: A single line like $.get() or $.post() can handle common use-cases.
Faster Development: jQuery speeds up prototyping and integrates well into existing HTML/JS projects.
Built-in JSON Handling: Easily send and parse JSON data with minimal configuration.
For projects that don’t need a full SPA framework or heavy dependency stacks, jQuery AJAX hits the sweet spot between simplicity and functionality.
jQuery AJAX Syntax Explained
At the heart of jQuery’s AJAX capabilities is the versatile $.ajax() method. It gives you full control over how your asynchronous requests are made, allowing you to specify everything from request type to headers, data payloads, and success/error handling.
Here’s the basic structure:
$.ajax({
url: 'https://api.example.com/data', // Endpoint you're calling
type: 'GET', // Request type: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE
data: { id: 123 }, // Data sent to the server (for GET or POST)
success: function(response) {
// What to do with the server's response
console.log('Success:', response);
},
error: function(xhr, status, error) {
// What to do on failure
console.error('Error:', error);
}
});Key Options Explained
url: The endpoint or file you’re communicating with.
type (or method): HTTP method like GET, POST, PUT, or DELETE.
data: Key-value pairs sent along with the request (optional).
success: A callback function executed when the request completes successfully.
error: A callback for handling failed requests or server errors.
dataType (optional): Expected format of the response, e.g., 'json', 'html', 'text'.
This method is ideal when you need full control and flexibility. For simpler use cases, jQuery also provides shorthand methods like $.get(), $.post(), and $.getJSON().
Quick & Easy AJAX Methods in jQuery
While $.ajax() offers full control, jQuery also provides simplified methods that make common AJAX tasks even quicker. These shorthand functions are perfect for most use cases and help keep your code clean and readable.
1. $.get(): Fetch Data with a GET Request
$.get('https://api.example.com/user', function(response) {
console.log('User data:', response);
});Use case: Fetch data from the server with minimal setup.
Behind the scenes: Equivalent to $.ajax({ type: 'GET' }).
2. $.post(): Send Data via POST
$.post('https://api.example.com/login', { username: 'john', password: '1234' }, function(response) {
console.log('Login response:', response);
});3. $.getJSON(): Automatically Parse JSON Responses
$.getJSON('https://api.example.com/stats', function(data) {
console.log('Stats:', data);
});Use case: When you know the server returns JSON — no need to manually parse the response.
When to Use Shorthands vs. $.ajax()
Use Case | Method to Use |
Quick API fetch | $.get() |
Simple form submission | $.post() |
JSON-only responses | $.getJSON() |
Need custom headers/config | $.ajax() |
These shorthand methods are beginner-friendly and keep your code concise—ideal for quick wins without sacrificing functionality.
Handling AJAX Responses Like a Pro
Making the request is just half the job—what you do with the response is what makes your web app dynamic and interactive. Here’s how to handle responses the smart way using jQuery AJAX:
1. Parse JSON Responses
jQuery automatically parses JSON when the response’s Content-Type is set to application/json. That means:
$.getJSON('https://api.example.com/data', function(data) {
console.log(data); // Already a JavaScript object
});No need to write JSON.parse() — jQuery does it for you.
2. Update the DOM Dynamically
Once you have the response data, you can use jQuery to inject it into the page:
$.getJSON('/api/user', function(user) {
$('#username').text(user.name);
$('#email').text(user.email);
});3. Handle Errors Gracefully
Always include error handling—users shouldn’t be left wondering what went wrong:
$.ajax({
url: '/api/data',
type: 'GET',
success: function(data) {
$('#content').html(data.message);
},
error: function(xhr, status, error) {
console.error('Error:', error);
$('#content').html('<p>Oops! Something went wrong.</p>');
}
});Bonus tip: You can access detailed error info via xhr.status and xhr.responseText.
Real-World Examples Using jQuery AJAX
To bring everything together, let’s look at real use cases where jQuery AJAX shines in everyday web development. These examples will show how to fetch data from a public API and update the page dynamically—without refreshing. Perfect for dashboards, user profiles, or news widgets.
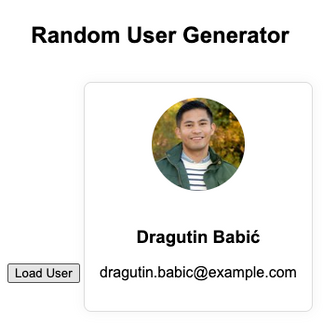
Example: Fetch and Display a Random User Profile
We’ll use the free Random User API to simulate pulling data from a server and updating the DOM with the user’s name, picture, and email.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>jQuery AJAX Example</title>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background: #ffffff;
padding: 2rem;
text-align: center;
}
#user-card {
border: 1px solid #ddd;
padding: 1rem;
border-radius: 8px;
display: inline-block;
margin-top: 1rem;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0,0,0,0.05);
}
#user-card img {
border-radius: 50%;
margin-bottom: 1rem;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Random User Generator</h2>
<button id="load-user">Load User</button>
<div id="user-card" style="display: none;">
<img id="user-img" src="" alt="User Image" width="100" height="100" />
<h3 id="user-name"></h3>
<p id="user-email"></p>
</div>
<script>
$('#load-user').on('click', function() {
$.ajax({
url: 'https://randomuser.me/api/',
method: 'GET',
success: function(response) {
const user = response.results[0];
$('#user-img').attr('src', user.picture.large);
$('#user-name').text(`${user.name.first} ${user.name.last}`);
$('#user-email').text(user.email);
$('#user-card').fadeIn();
},
error: function() {
alert('Failed to load user. Try again.');
}
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
Conclusion: Making the Web Dynamic, One AJAX Call at a Time
Even in a modern JavaScript ecosystem filled with frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular, jQuery's AJAX functionality still holds its ground for many practical reasons—simplicity, reliability, and broad browser support. Whether you're working on a legacy codebase or quickly prototyping dynamic features, jQuery AJAX offers a clean and efficient way to communicate with the server asynchronously.
By mastering jQuery’s AJAX capabilities, you unlock smoother user experiences, reduce page reloads, and build truly interactive web applications—all with just a few lines of code.
So the next time you need to send or receive data without a full-page refresh, don’t overlook the power of good old jQuery AJAX.